Architecture Overview
System Properties
The overall design is intended to operate as an adjunct execution pipeline that remains isolated from core AMM mechanics. When no profitable opportunity is present, the pipeline remains inactive and imposes no additional cost.
Key characteristics include:
- Atomicity: backrun execution and settlement occur within the same transaction as the initiating swap.
- Zero mempool exposure: no step of the process is broadcast or observable externally.
- No reentrancy risk: execution conforms to AMM-defined callback safety constraints.
- Full compatibility: integrates with AMM architectures that support post-swap hooks without modifying their internal logic.
Components
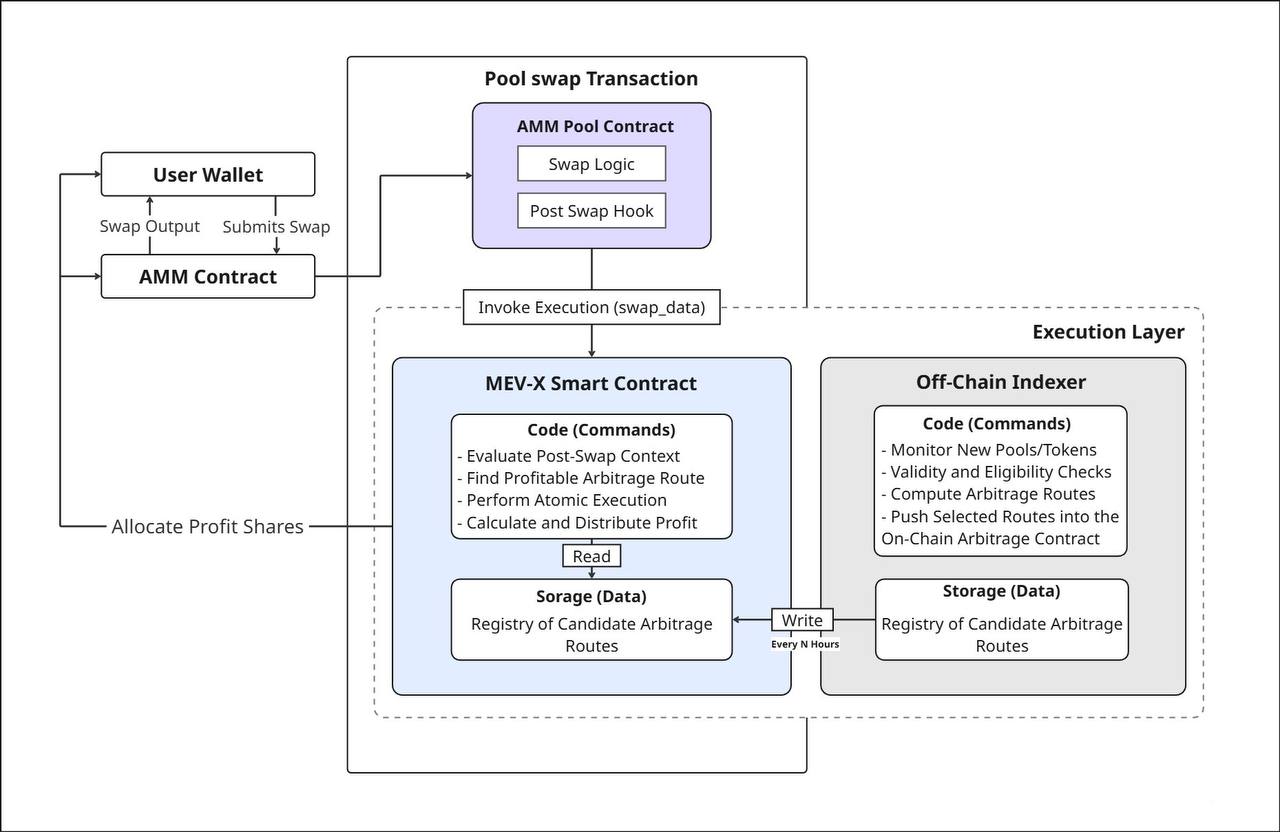
The system consists of three primary components that work together to identify, execute, and settle arbitrage opportunities created by user trades.
1. Post-Swap Hook Layer
The hook integrates at the pool level and is invoked through the AMM’s native post-swap callback mechanism. Architectures such as Uniswap v4, Algebra Integral, and PancakeSwap Infinity expose standardized lifecycle hooks that execute immediately after a swap updates pool balances.
Once triggered, the hook forwards the post-swap event to the execution layer in a deterministic, non-reentrant manner, enabling the MEV internalization pipeline to begin without altering pool logic or user-visible behavior.
2. Execution Layer
The execution layer receives the post-swap event and evaluates whether the updated pool state permits a profitable backrun. This component operates entirely within the transaction boundary and does not interact with the public mempool.
Its objective is to determine, construct, and execute an arbitrage path with guaranteed atomicity. The module applies route constraints, token validation, and safety checks before initiating any action.
If a viable opportunity is detected, the execution layer performs the backrun through an internally orchestrated swap sequence. If profitability or safety conditions are not met at any point, the hook reverts without side effects on the user’s swap.
3. Settlement Path
Once the arbitrage route completes, the settlement path finalizes the outcome inside the same transaction. It calculates the net surplus and applies the platform’s configured distribution model, allocating returns among the designated recipients.
All transfers are executed using standard ERC-20 mechanisms and occur before the outer transaction completes. Settlement remains fully contained within the transaction boundary defined by the execution layer.